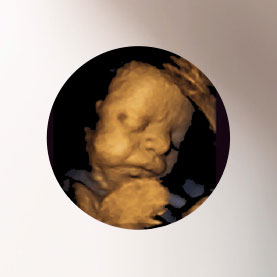
Prenatal diagnostics are a cornerstone of modern prenatal care, which I have been closely involved with for many years. These scans and examinations are very comprehensive. In addition to high-end, specialised equipment, they demand a great deal of experience and special training. Regular participation in congresses in Germany and abroad ensures that my knowledge and skills stay right up-to-date.
-
First trimester screening (nuchal translucency scan)
The first trimester screening is a well-established, non-invasive scan during early pregnancy, used to assess individual risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the unborn fetus.
If conditions are good when this scan is carried out, it provides information on how your child is developing.
-
Organ scan (high resolution ultrasound) 20-23 weeks
With a further, high resolution ultrasound scan, which is usually carried out between the 20th and 23rd week of pregnancy, it is possible to check for a great number of developmental abnormalities and organ defects, some of which cannot be detected during early pregnancy. This ultrasound scan is far more comprehensive than that provided for in the German Maternity Guidelines during this period. In addition to specialised, high-end equipment, it is essential that the medical specialist have a great deal of experience.
This detailed diagnostic scan includes an assessment of how the foetus is developing given the stage in pregnancy, the morphology of the individual organs, an assessment of the baby’s heart including the large blood vessels, the morphology and position of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid.
-
NIPT (non-invasive prenatal test)
This test involves extracting the unborn child’s genetic material (DNA) from the mother’s blood. This supplements the non-invasive test procedure. All that is necessary is a blood sample from the mother-to-be.
The majority of trisomy 13, 18 and 21 cases can be detected by the NIPT, as well as anomalies affecting sex chromosomes (as found for example in cases of Turner Syndrome).
-
Fetal Doppler ultrasound
With fetal Doppler ultrasound, it is possible to carry out an especially detailed scan of your fetals blood circulation, showing the direction and speed of the circulating blood. This scan plays an important role in prenatal diagnostics for:
- Possible developmental abnormalities
- Possible preeclampsia
- Suspected heart defects
- Abnormal fetal heartbeat (CTG)
- Gestational diabetes (maternal diabetes during pregnancy)
With the aid of a Doppler ultrasound, information can be garnered on the blood supply to the fetus, as well as heart and circulatory function, so that risks can be recognised early on and appropriate treatment begun.
Fetal echocardiography is a special type of Doppler ultrasound, which enables congenital heart defects to be diagnosed. In order to carry out a fetal echocardiography, the medical specialist needs to be highly qualified, experienced and have access to high resolution ultrasound equipment.
-
3D-/4D ultrasound
3D ultrasound enables you to see a three-dimensional picture of your baby. If the child’s movements are also recorded, this is referred to as a 4D ultrasound. This technology allows the child’s movements to be shown in real-time, in almost photographic quality. The emotional connection with the child can be strengthened through the three dimensionality of the picture, contributing to the parent-child bonding process. Additionally, 3D ultrasound broadens the options for diagnostics and medical treatment.
The best time for this scan is between the 26th and 30th week of pregnancy. However, whether clear photos can be obtained depends a great deal on the position of the child, the amount of amniotic fluid and visual and sonographic conditions.
Public health insurers do not cover the costs of a 3D ultrasound.
-
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia can arise during the second half of pregnancy. This is a very serious complication. The symptoms are high blood pressure in the mother, as well as increased levels of proteins being excreted by the kidneys, causing water retention (oedema).
This can reduce the circulation of blood to the placenta, leading to the fetus not receiving everything they need. Early preeclampsia arises before the 34th week; late preeclampsia presents after the 34th week.
The early form of preeclampsia is very serious and presents an acute risk to mother and child. If, thanks to screening, an increased risk of preeclampsia is recognised at an early stage, then the expectant mother can be monitored more closely. This screening takes place between the 11th and 14th weeks of pregnancy, via an additional measurement of the expectant mother’s blood pressure, a special ultrasound scan of the blood vessels in the womb (Aa. uterinae) and by testing for two kinds of proteins in the mother’s blood – pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (pregnancy-associated plasma protein A) and PlGF (placental growth factor).
If the tests find that there is an increased risk, 100mg of aspirin can be prescribed as a preventative measure well before the 16th week; this prevents over 50% of preeclampsia cases. This screening is carried out at the same time as the first semester screening, meaning that you can choose to have both scans carried out during the same consultation.
Diagnosis of preeclampsia mainly depends on clinical signs. Two markers: sFlt-1 (soluble fms-like-tyrosine kinase-1) and PlGF (placental growth factor) can confirm a suspected case of acute preeclampsia or risk of preeclampsia. Recognising preeclampsia at an early stage enables appropriate action to be taken to care for both mother and child.